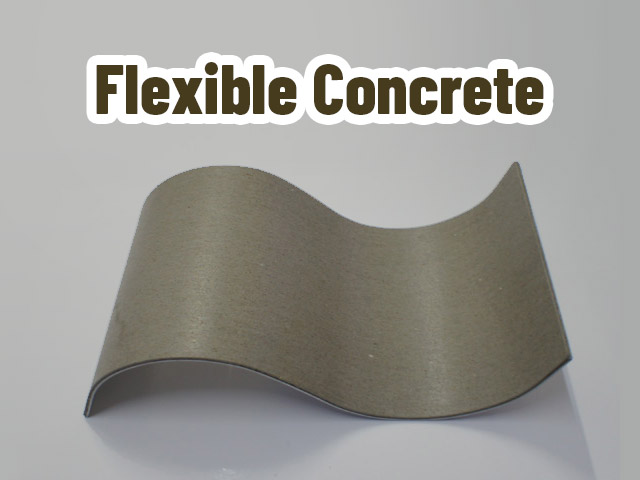
Unlikely conventional concrete, flexible concrete is a cement-containing composite material designed to have the stretchable materials. In order to reach a more flexible structure, flexible concrete is obtained by making some changes in the materials of traditional concrete production.
Flexible concrete is developed by Professor Victor C. Li, an academic member of Civil and Environmental Engineering Department in the the University of Michigan. In this article, we will give information about the substances used in the preparation, its features and in which areas it is used.
What is Flexible Concrete?
Flexible concrete, also known as bendable concrete, is obtained by removing coarse aggregates and adding more fiber into the mixture. In other words, substances with plasticizing effect are added to mixture containing cement, fiber, sand and water. Some of these materials can be explained as follows:
- Fiber: Silica, asbestos, glass or steel fibers are used. These fibers are what provide the flexibility of concrete. Another function of fiber is to support the strength of concrete. Portland cement used in traditional concrete production can also be used.
- Aggregates: The use of fine sand is the ideal aggregate for flexible concrete manufacture. Different materials such as normal sand, slag, ash can also be used.
- Plasticizing agents: The use of flexible concretes in structures requires it to be more easily workable. At this stage, lignin, naphthalene, melamine formaldehyde, sulfonate, polycarboxylate ether and lignosulfonates are used, which have a plasticizing effect.
In order to understand what effects these substances have, the properties of flexible concrete should be examined.
Properties
The properties of bendable concrete used in construction of road, bridge, and earthquake resistant buildings as well as concrete manufacturing are as follows:
- Tensile strength ranges from 10 to 15 MPa.
- Compressive strength can be up to 70 MPa.
- The cements used in its construction helps to fill small cracks that have previously formed by reacting with rain water. So it has the feature of self-
- The strain-related deformability rate is between 3 and 5 percent.
- The strain capacity of flexible concrete is about 300 times higher than traditional concrete. It comes to the fore with this feature.
Thus, flexible concretes has high stretchability and high durability. It does not cause harmful gas emission like traditional concrete. It does not crack. Despite this durability, it is around 30 percent lighter than conventional concrete. It also reduces costs because of less steel usage in construction.
Comparison of Traditional Concrete with Flexible Concrete
| Traditional Concrete | Flexible Concrete |
| It is fragile | It is bendable |
| Less durable | More durable |
| It cannot self-repair | It can self-repair |
| Cracks may occur over time | Fewer cracks occur than conventional concrete. |
| It has a curing period of 28 days | It has a curing period of 7 days |
| It is manufactured using unskilled labor | It requires skilled personnel and engineering |
| It is produced from materials that are more available on the market | Finding high quality of fiber is more difficult |
| Initial cost of construction is low | Initial cost of construction is higher |
| It requires more steel use | It requires no steel use |
| It has low cracking resistance | It has high cracking resistance |
| Heavier structures are obtained | 30 percent lighter structures are obtained |
| It causes the release of harmful gases during construction | It provides less harmful gas emission |
